Radiant floor heating is an efficient and comfortable way to warm your home, and with a radiant floor heating diagram, you can gain a deeper understanding of how it works. By visualizing the system’s components and their interactions, you can better appreciate the mechanics behind this popular heating method. Let’s explore the different aspects of radiant floor heating and how a diagram can help you comprehend your system.
- There are open and closed systems in radiant floor heating, each with its own advantages and considerations.
- Choosing the right heat source for your radiant floor heating system is crucial and depends on your specific requirements.
- Maintaining proper pressure and purging air from the system is essential to prevent issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Incorporating a whole-house filter can protect system components and plumbing fixtures from damage.
- Efficient circulator pumps, such as the ALPHA series, can significantly reduce energy costs and enhance system performance.
Now that we’ve covered the basics let’s dive deeper into the workings of radiant floor heating and explore the different types of systems in Section 2.
How Does Radiant Floor Heating Work?
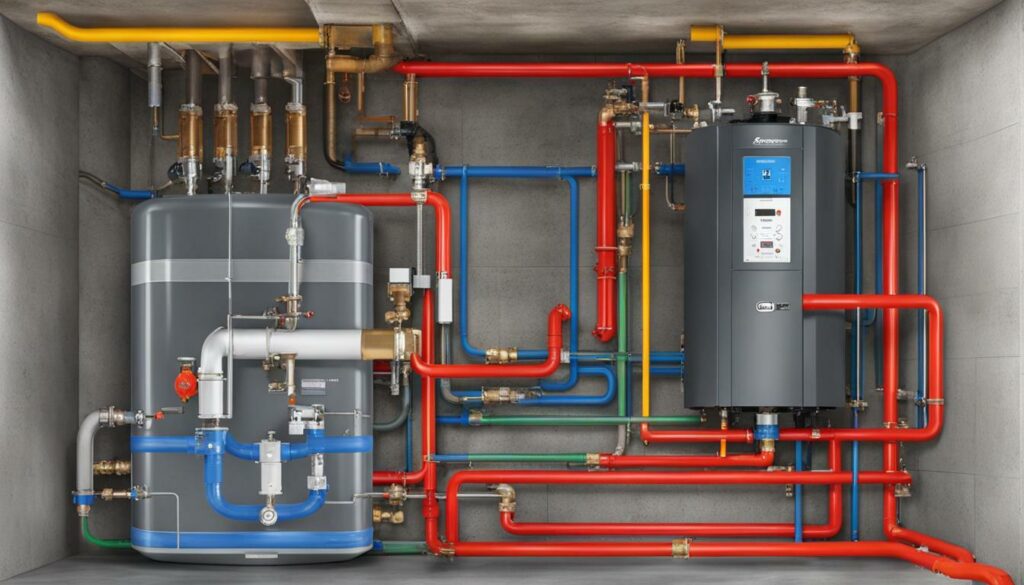
Radiant floor heating works by circulating warm water through pipes or electric heating elements installed beneath the floor, providing a steady and comfortable heat source. The radiant floor heating diagram below illustrates the basic setup of a typical system.
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat source | It can be an on-demand water heater, tank-type water heater, boiler, or electric unit, depending on specific requirements. |
| Pipes or heating elements | Installed beneath the floor, usually embedded in a concrete slab or mounted on subflooring. |
| Circulator pump | Forces the heated water to circulate through the pipes or heating elements. |
| Thermostat | Controls the temperature of the system and maintains the desired level of warmth. |
When the system is activated, the heat source warms the water which is then pumped through the pipes or heating elements. The warm water radiates heat through the flooring, creating a comfortable environment. As the heat dissipates, the cooler water returns to the heat source to be reheated and recirculated.
It’s important to note that radiant floor heating can be installed using different types of systems: open and closed. Open systems use the same water for domestic hot water and floor heating, while closed systems have a dedicated heat source and use a closed-loop system with antifreeze as the heat transfer medium.
Types of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
There are various types of radiant floor heating systems, each with its own benefits and considerations, as depicted in the radiant floor heating diagram.
In an open system, the same water that is used for domestic hot water also circulates through the radiant floor. This is a very efficient setup since one heat source serves both purposes. However, standby losses and two heat sources can be a drawback. On the other hand, closed systems use a dedicated heat source for the radiant floor and the fluid circulates in a closed loop. This allows the use of antifreeze as the heat transfer medium, which is beneficial in areas prone to power outages or freezing temperatures.
When it comes to choosing a heat source, there are various options available. On-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, and electric units are all suitable choices, depending on the specific requirements.
| Type of Radiant Floor Heating System | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Open System | Efficient, one heat source for hot water and radiant floor heating | Standby losses, two heat sources |
| Closed System | Use of antifreeze, suitable for areas with power outages or freezing temperatures | A dedicated heat source is required |
It’s important to consider the type of antifreeze to be used and its concentration in the system. Manufacturers provide guidelines for the appropriate mixture, and it is recommended to premix the antifreeze before pumping it into the system. Moreover, maintaining proper pressure in the system is crucial to prevent air from entering. Air can cause issues and should be purged during start-up.
Additionally, the use of a mixing valve is important in systems where the heat source supplies water at a higher temperature than required by the radiant floor. This ensures that the water is tempered to a suitable temperature before entering the radiant system.
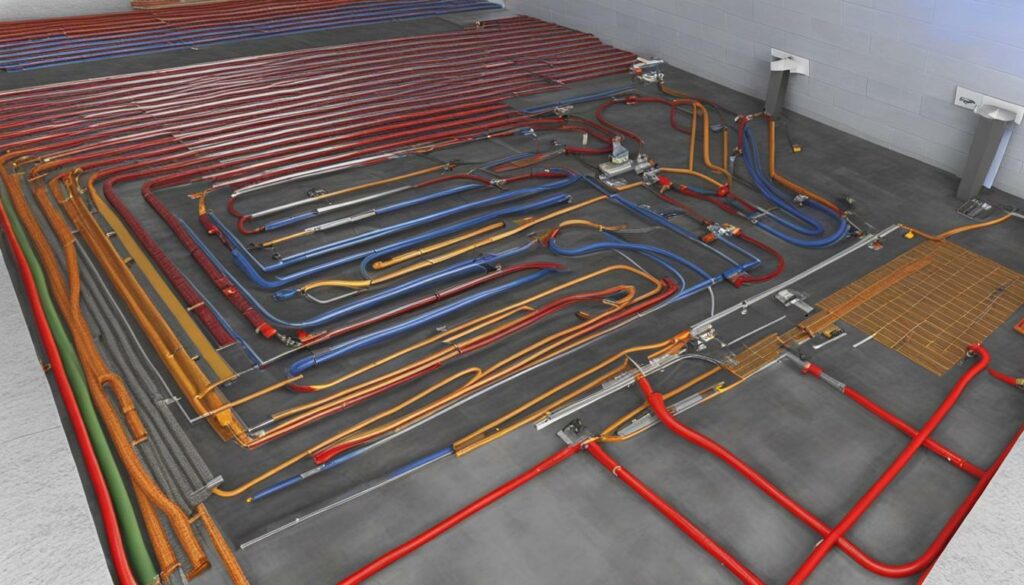
The installation of a whole-house filter can protect components in open systems and plumbing fixtures from damage caused by the water’s mineral content and additives like chlorine. It is also worth considering the quality of the water supply from municipal sources and the use of a separate heat exchanger system if the water contains high concentrations of chlorine.
Understanding the different components and considerations will help ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your radiant floor heating system.
Components of a Radiant Floor Heating System
A radiant floor heating system consists of several components, including a heat source, pipes or electric heating elements, a circulation pump, and controls, as illustrated in the radiant floor heating diagram below:
The heat source can vary depending on the specific system requirements and can include options such as on-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, or electric units. This heat source is responsible for providing the necessary warmth to the system.
The pipes or electric heating elements, commonly referred to as the “in-floor heating system,” are responsible for distributing heat evenly throughout the floor. These components are strategically installed below the floor’s surface, allowing the heat to radiate upwards and warm the room.
The circulation pump is an essential component that helps circulate the fluid within the system, ensuring optimal heat transfer. This pump works in conjunction with the controls, which regulate the temperature and operation of the system. The controls can include thermostats, timers, and other devices that allow users to adjust and manage the heating system according to their preferences.
Key Components of a Radiant Floor Heating System:
- Heat source (on-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, electric units)
- Pipes or electric heating elements
- Circulation pump
- Controls (thermostats, timers, etc.)
Understanding the role of each component in a radiant floor heating system is crucial for ensuring the system’s efficiency and reliable performance. By familiarizing yourself with the radiant floor heating diagram and the components involved, you can make informed decisions during installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting processes.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heat source | Provides warmth to the system |
| Pipes or electric heating elements | Distributes heat evenly throughout the floor |
| Circulation pump | Circulates the fluid for optimal heat transfer |
| Controls | Regulate temperature and operation of the system |
Radiant Floor Heating Installation
Installing a radiant floor heating system requires careful planning and consideration, as shown in the radiant floor heating diagram. Understanding the various components and considerations involved will help ensure a successful installation and optimal performance of your heating system.
One of the first steps in the installation process is determining the type of system that best suits your needs. This could be an open system, where the same water used for domestic hot water also circulates through the radiant floor, or a closed system, which uses a dedicated heat source and a closed loop for fluid circulation.
Next, you’ll need to choose the appropriate heat source for your radiant floor heating system. Options range from on-demand water heaters and tank-type water heaters to boilers and electric units. Consider the specific requirements of your home to determine the most suitable heat source for efficient and consistent heating.
During installation, it’s important to ensure the proper mixture and concentration of antifreeze in the system, especially in closed systems. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and pre-mixing the antifreeze before pumping it into the system are recommended practices. Additionally, maintaining the correct pressure in the system is crucial to prevent air from entering, which can cause issues and should be purged during start-up.
The use of a mixing valve is essential in systems where the heat source supplies water at a higher temperature than required by the radiant floor. The mixing valve helps temper the water to a suitable temperature before it enters the radiant system, ensuring optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
Lastly, it is worth considering the installation of a whole house filter, especially in open systems, to protect components and plumbing fixtures from damage caused by the water’s mineral content and additives like chlorine. This can help prolong the lifespan of your system and ensure its efficient operation.
By following these guidelines and considering the specific requirements of your home, you can install a radiant floor heating system that provides consistent, energy-efficient, and comfortable heating throughout your living spaces.
Radiant Floor Heating Design
Proper design is crucial for an effective and efficient radiant floor heating system, as depicted in the radiant floor heating diagram. To ensure optimal performance and comfort, several factors must be considered during the design process.
One key aspect is determining the heat load of each room or zone. This involves calculating the amount of heat required to maintain the desired temperature in each area. Factors such as room size, insulation, and desired temperature levels play a significant role in this calculation.
Another important consideration is the spacing of the radiant floor heating pipes. The spacing should be determined based on the heat output of the system and the floor covering used. Generally, closer pipe spacing is recommended for areas with higher heat loss or where a faster response time is desired.
Zoning is also an essential aspect of radiant floor heating design. Dividing the system into zones allows for independent temperature control in different areas of the house. This enables energy savings by only heating occupied spaces and provides personalized comfort for each occupant.
Additionally, including a mixing valve in the design is recommended when the heat source supplies water at a higher temperature than required by the radiant system. The mixing valve ensures that the water is tempered to a suitable temperature before circulating through the radiant floor, preventing overheating and potential discomfort.
| Type of Design Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Heat Load Calculation | Consider room size, insulation, and desired temperature levels to determine the heat load for each zone. |
| Pipe Spacing | Determine the optimal spacing of the radiant floor heating pipes based on heat output and floor covering. |
| Zoning | Create zones to independently control temperature in different areas of the house, maximizing energy efficiency and comfort. |
| Mixing Valve | Include a mixing valve to temper the water temperature before it enters the radiant floor system, preventing overheating. |
By considering these design factors and utilizing a radiant floor heating diagram as a visual guide, you can create a system that provides efficient, comfortable, and customizable heating throughout your home.
Benefits of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating offers numerous benefits for homeowners, as illustrated in the radiant floor heating diagram. This heating system provides consistent warmth throughout your home by delivering heat directly to the floor, resulting in a comfortable and cozy living environment. Unlike traditional forced air systems, which can create uneven heating and drafts, radiant floor heating ensures that every corner of your home is evenly heated. This eliminates cold spots and creates a more enjoyable living space for you and your family.
One of the key advantages of radiant floor heating is its energy efficiency. By utilizing the natural process of radiant heat transfer, this system requires lower operating temperatures compared to forced air systems. This not only reduces energy consumption but also helps to lower your utility bills. In fact, studies have shown that radiant floor heating can save homeowners up to 30% on their heating costs.
In addition to energy efficiency, radiant floor heating offers improved air quality. Unlike forced air systems that can circulate dust, allergens, and other pollutants throughout your home, radiant floor heating operates silently and without any air movement. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals with respiratory conditions or allergies, as it minimizes airborne particles and promotes a healthier indoor environment.
Furthermore, radiant floor heating provides design flexibility and eliminates the need for bulky radiators or baseboard heaters. With the heat emanating from the floor, you have more freedom to arrange furniture and decorate your space without any obstructions. This clean and streamlined aesthetic adds a touch of elegance to your home while maximizing usable living space.

Overall, radiant floor heating offers a range of benefits, including improved comfort, energy efficiency, better air quality, and design flexibility. Whether you are building a new home or renovating your existing space, consider the advantages of radiant floor heating and how it can enhance your lifestyle.
Radiant Floor Heating Vs. Forced Air
Radiant floor heating and forced air systems have distinct characteristics, as shown in the radiant floor heating diagram. Each system has its own advantages and considerations, making them suitable for different situations.
Radiant Floor Heating:
In a radiant floor heating system, heat is emitted from the floor and radiates upwards, warming the objects and people in the room. This type of heating provides consistent and comfortable warmth with no drafts or hotspots. It also eliminates the need for ductwork, reducing the potential for heat loss and improving energy efficiency.
Radiant floor heating operates silently, making it an excellent choice for bedrooms, nurseries, and living areas where peace and quiet are desired. It also allows for greater design flexibility since there are no registers or radiators to consider when arranging furniture or decorating.
Forced Air:
Forced air systems, on the other hand, rely on ductwork to distribute heated air throughout a space. These systems use a furnace or heat pump to generate warm air, which is then propelled through vents or registers into the rooms.
Forced air heating is known for its quick response time, rapidly raising the temperature in a room. It can also accommodate the addition of air conditioning, providing both heating and cooling functions. However, forced air systems can be noisier than radiant floor heating systems and may cause uneven heating if not properly balanced.
When choosing between radiant floor heating and forced air, consider factors such as your heating preferences, energy efficiency goals, and the design of your home. Both systems have their advantages and can provide effective heating solutions based on your individual needs and preferences.
| Aspect | Radiant Floor Heating | Forced Air |
|---|---|---|
| Comfort | Consistent and comfortable warmth | Quick response time, but may cause uneven heating |
| Noise Level | Silent operation | Potential noise from vents and registers |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduced heat loss, improved efficiency | Efficient if properly balanced |
| Design Flexibility | No visible registers or radiators | Requires ductwork |
Conclusion
Choosing between radiant floor heating and forced air depends on your priorities and the specific requirements of your home. Consider factors such as comfort, noise level, energy efficiency, and design flexibility to make an informed decision. With a radiant floor heating diagram and an understanding the characteristics of each system, you can select the heating solution that best suits your needs and preferences.
Radiant Floor Heating Under the Carpet
Radiant floor heating can be successfully installed under carpeted floors for a cozy and comfortable living space, as seen in the radiant floor heating diagram. This type of heating system provides several benefits, including even heat distribution, energy efficiency, and reduced allergens compared to traditional forced air systems.
When installing radiant floor heating under carpet, it is essential to choose carpet and carpet padding with a low thermal resistance to allow for effective heat transfer. Thicker carpets or those with excessive insulation may hinder the heat flow, reducing the system’s efficiency. It’s recommended to consult with a professional installer to ensure the right carpet and padding combination for optimal performance.
The installation process involves placing a radiant floor heating system beneath the subfloor, which then radiates heat upwards to warm the carpeted surface. The system consists of a network of pipes or electric heating elements embedded in a thermal mass, such as concrete or specialized panels. These components work together to heat the floor and provide a comfortable warmth throughout the room.
| Benefits of Radiant Floor Heating Under Carpet: |
|---|
| 1. Energy Efficiency: Radiant floor heating operates at lower temperatures compared to forced air systems, resulting in energy savings and reduced utility bills. |
| 2. Enhanced Comfort: With radiant floor heating, heat is evenly distributed throughout the room, eliminating cold spots and providing a cozy environment. |
| 3. Allergen Reduction: Unlike forced air systems, radiant floor heating does not circulate allergens, dust, or other particles, helping to maintain better indoor air quality. |
| 4. Design Freedom: Radiant floor heating allows for greater design flexibility in terms of furniture placement and room layout, as there are no visible radiators or air vents. |
It’s important to note that the installation of radiant floor heating under carpeted floors should be carried out by experienced professionals to ensure proper installation and avoid any potential damage to the heating system or flooring. Professional installers will be able to determine the appropriate heat output spacing of heating elements and recommend the best type of flooring for optimal performance.
In conclusion, radiant floor heating can be successfully installed under carpeted floors, offering energy-efficient, comfortable, and allergen-free heating for your home. With the right carpet and professional installation, you can enjoy the benefits of radiant floor heating while maintaining a cozy and inviting living space.
Radiant Floor Heating Cost
While radiant floor heating offers numerous benefits, it is important to consider the cost implications, as reflected in the radiant floor heating diagram. The cost of installing a radiant floor heating system varies depending on various factors, including the size of the space, the type of system chosen, and the specific requirements of the installation. However, the long-term savings and energy efficiency of radiant floor heating often outweigh the initial investment.
When it comes to the cost of materials, radiant floor heating systems typically require piping, a heat source (such as a boiler or water heater), and controls. The cost of these components can vary depending on the quality and brand chosen. Additionally, the installation process may involve labor costs if you choose to hire a professional.
| Component | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Radiant Floor Heating System | $3 to $10 per square foot |
| Boiler or Water Heater | $1,000 to $5,000 |
| Piping and Controls | $1,000 to $3,000 |
| Installation | $2 to $6 per square foot |
It is important to note that the cost of installation can vary depending on the complexity of the project and any additional factors that may need to be taken into account, such as subfloor preparation or modifications to existing structures.
While the initial investment may be higher than other heating systems, radiant floor heating offers long-term savings through energy efficiency. The even distribution of heat throughout the space reduces energy waste and minimizes the need for additional heating sources. This can result in lower utility bills over time and increased comfort in your home.
Before making a decision, it is recommended to consult with a professional to determine the specific cost implications for your individual needs. They can assess your space, provide an accurate cost estimate, and guide you through the installation process to ensure a successful and cost-effective solution.
Maintaining a Radiant Floor Heating System
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your radiant floor heating system running smoothly, as indicated in the radiant floor heating diagram. By following a few simple steps, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your system.
Firstly, it is essential to check the pressure gauge on your system regularly. The ideal pressure range is typically between 12-15 psi. If the pressure drops below this range, it may indicate a leak in the system. Contact a professional to locate and repair the leak promptly.
Another essential maintenance task is to flush and clean the system periodically. Over time, sediment and debris can accumulate in the pipes, causing reduced efficiency and potential damage. Flushing the system with a cleaning solution will help remove any buildup and ensure smooth operation. Consult with a heating professional for the recommended cleaning products and procedures for your specific system.
In addition to flushing, it is essential to replace the system’s filter regularly. The filter traps any particles present in the water supply, preventing them from clogging the pipes or damaging the components. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the recommended filter replacement schedule and follow it diligently.
Finally, having your radiant floor heating system professionally inspected and serviced at least once a year is essential. A professional technician can identify any issues or potential problems before they escalate, saving you from costly repairs down the line. They will also ensure that all components are functioning correctly and make any necessary adjustments or repairs.
By following these maintenance practices, you can enjoy the efficient and comfortable heating provided by your radiant floor heating system for years to come.
- Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of your radiant floor heating system.
- Check the system’s pressure regularly and address any drops below the recommended range to prevent leaks.
- Flushing and cleaning the system periodically removes sediment and debris, ensuring efficient operation.
- Replace the system’s filter according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent clogs and damage.
- Have your system professionally inspected and serviced annually to catch any issues before they worsen.
Table: Recommended Maintenance Schedule
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check system pressure | Monthly |
| Flush and clean the system | Annually |
| Replace system filter | As per the manufacturer’s instructions |
| Professional inspection and servicing | Annually |
Efficient Circulator Pumps for Radiant Floor Heating
Upgrading to efficient circulator pumps can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your radiant floor heating system, as depicted in the radiant floor heating diagram. These pumps play a crucial role in circulating the heat transfer fluid through the system, ensuring optimal heat distribution and comfort in your home.
Efficient circulator pumps, such as the ALPHA series, are designed to minimize energy consumption while providing reliable performance. These pumps utilize advanced variable speed technology, allowing them to adjust their speed based on the heating demand. By operating at lower speeds when less heat is required, they consume less electricity and reduce energy waste.
In addition to energy savings, efficient circulator pumps also offer other benefits. They are designed for quiet operation, ensuring a peaceful and undisturbed living environment. Their compact size and easy installation make them ideal for both new construction and retrofit projects. With their durability and long lifespan, these pumps provide a reliable solution for your radiant floor heating system.
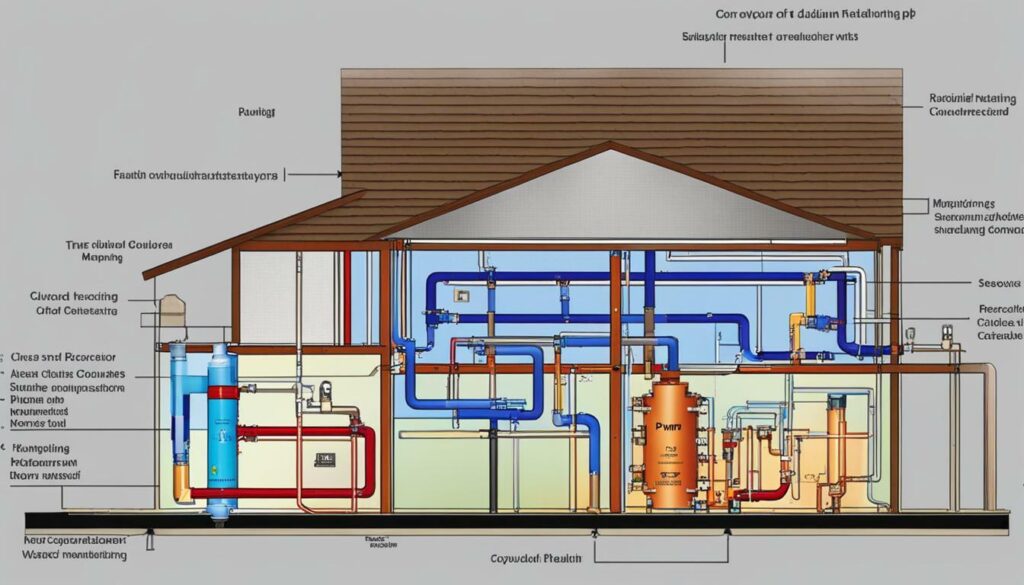
Upgrade to efficient circulator pumps for your radiant floor heating system and experience improved energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
Whole House Filtration for Open Systems
Installing a whole house filtration system can help maintain the performance and longevity of your radiant floor heating system, as shown in the radiant floor heating diagram. In open systems, where the same water circulates through both the radiant floor and domestic hot water, it becomes important to address the potential issues caused by the water’s mineral content and additives like chlorine. The use of a whole-house filter can effectively prevent damage to the system’s components and plumbing fixtures.
Minerals present in the water supply can lead to the accumulation of scale and deposits in the radiant tubing, reducing the system’s efficiency over time. Additionally, chlorine and other chemicals used for water treatment can have a corrosive effect on the pipes and other components, potentially leading to leaks or premature failure.
By incorporating a whole house filtration system, you can remove impurities from the water before it enters the radiant floor heating system. This not only helps maintain the performance of the system but also improves the quality of water throughout your home. A clean and balanced water supply can greatly extend the lifespan of the system and prevent costly repairs or replacements in the future.
| Filtration System Benefits | Whole House Filtration |
|---|---|
| Protects components from mineral buildup | ✓ |
| Prevents corrosion caused by chlorine | ✓ |
| Improves water quality throughout the home | ✓ |
| Extends the lifespan of the radiant floor heating system | ✓ |
When selecting a whole-house filtration system, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your radiant floor heating system. Some filters are designed to address particular concerns, such as removing sediments, chemicals, or heavy metals. Consulting with a professional or contacting the manufacturer of your radiant floor heating system can help you determine the most suitable filtration solution for your needs.
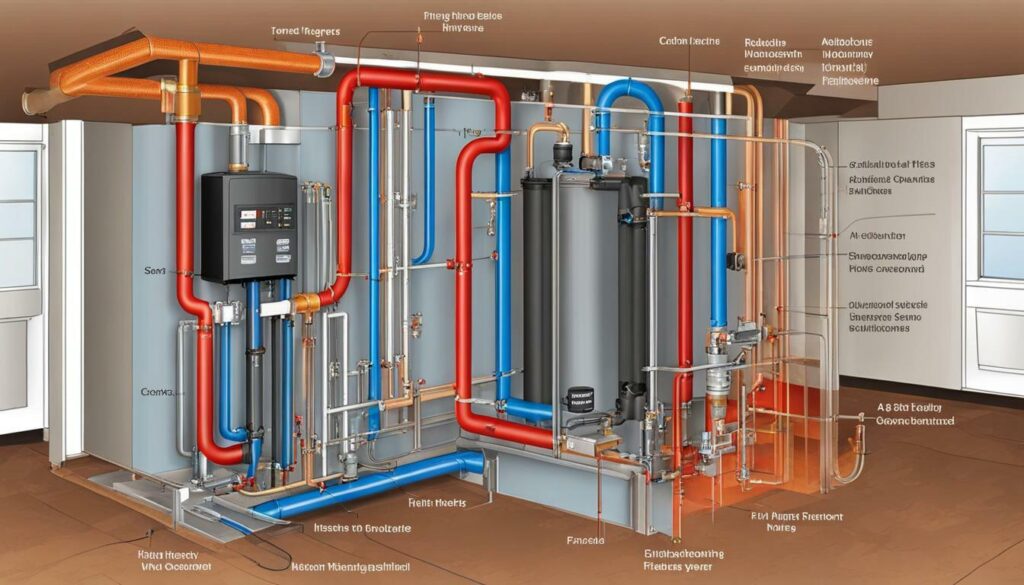
By investing in a whole-house filtration system, you can ensure that your open system remains in optimal condition, providing efficient and reliable heating for years to come. With clean and purified water flowing through your radiant floor heating system, you can enjoy the comfort and energy-efficiency benefits without worrying about mineral buildup or corrosion.
Considerations for Specific Plumbing Configurations
Certain radiant floor heating setups require specific plumbing configurations to ensure optimal performance, as outlined in the radiant floor heating diagram. Understanding these considerations is crucial for a successful installation and efficient operation of your system.
In open systems, where the same water circulates through the radiant floor and is also used for domestic hot water, it is important to address potential challenges. One such challenge is standby losses, which occur when the water heater or boiler runs to maintain the temperature, even when there is no demand for hot water. To mitigate these losses, installing a hot water recirculation system can help ensure quick access to hot water while conserving energy.
Another consideration is the presence of air in the system. Air can cause issues, including reduced efficiency and uneven heating. To prevent air from entering the system, it is important to install an air eliminator and purge the system of air during start-up. Proper pressure maintenance is crucial as well, as low pressure can result in air infiltration.
| Type of System | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Open System | – Efficient use of heat source – Dual-purpose for domestic hot water – Suitable for areas with stable power supply |
– Standby losses – Two heat sources – Potential for water quality issues |
| Closed System | – Antifreeze use for freeze protection – Dedicated heat source for radiant floor – Suitable for areas prone to power outages or freezing temperatures |
– Additional heat source required – Complexity of closed loop |
For both open and closed systems, selecting the appropriate heat source is essential. The choice will depend on factors such as energy efficiency, fuel availability, and personal preference. Common options include on-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, and electric units. Consulting with a professional can help determine the best heat source for your specific needs.
When installing a radiant floor heating system, incorporating a whole-house filter is recommended, especially in open systems. This helps protect the system components and plumbing fixtures from damage caused by the water’s mineral content and additives like chlorine. It is also advisable to consider the quality of the water supply from municipal sources and, if necessary, use a separate heat exchanger system to avoid potential issues caused by high chlorine levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the specific plumbing configurations for your radiant floor heating system is vital to ensure its optimal performance. By considering the type of system, heat source, potential air infiltration, and the use of filtration systems, you can experience efficient and reliable heating while prolonging the lifespan of your system. Consulting with a professional installer will help you navigate these considerations and ensure a successful installation.
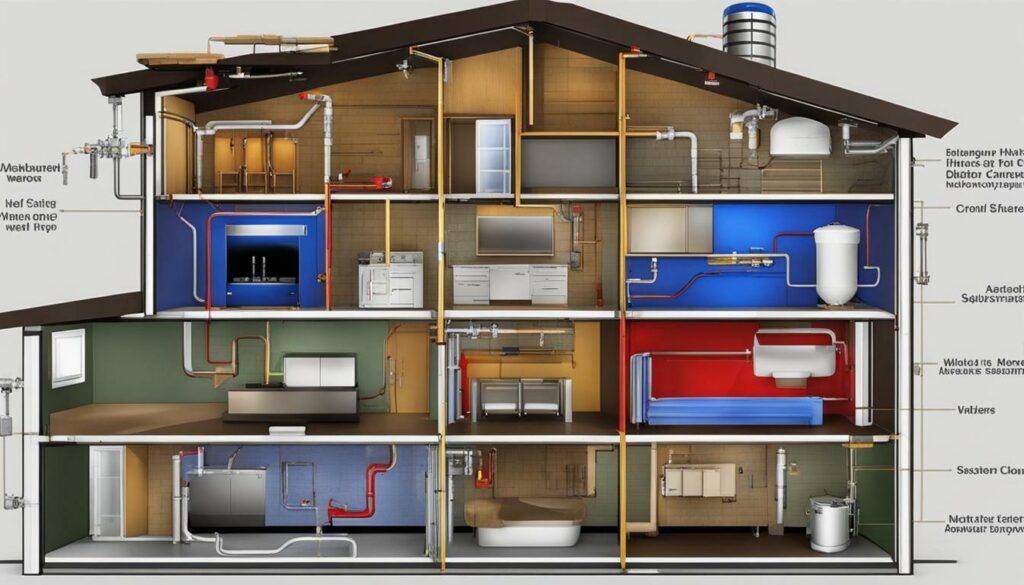
By using a radiant floor heating diagram and understanding the various components and considerations, you can optimize the performance and efficiency of your radiant floor heating system. With the knowledge gained from the diagram, you can make informed decisions about the type of system that best suits your needs.
Open systems offer the advantage of using the same water for both domestic hot water and radiant floor heating. However, closed systems provide the benefit of using antifreeze as the heat transfer medium, which is particularly advantageous in areas prone to power outages or freezing temperatures.
When choosing a heat source, consider options such as on-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, or electric units, depending on your specific requirements. It’s also crucial to ensure the proper mixing and concentration of antifreeze, as well as maintaining the correct pressure and purging any air from the system.
Installing a whole-house filter can protect the components in open systems and plumbing fixtures from potential damage caused by the mineral content and additives in the water. Consider incorporating efficient circulator pumps, like the ALPHA series, which can reduce energy costs and enhance system performance for optimal energy efficiency.
For high-volume systems and outdoor wood boilers, specific plumbing configurations should be followed to ensure optimal function and efficiency. By considering these factors and utilizing a radiant floor heating diagram, you can enjoy the benefits of a well-designed and properly maintained radiant floor heating system.
FAQ
What are the different types of radiant floor heating systems?
There are open and closed systems, each with its advantages and considerations.
What is the difference between open and closed radiant floor heating systems?
In an open system, the same water used for domestic hot water also circulates through the radiant floor. Closed systems use a dedicated heat source for the radiant floor, and the fluid circulates in a closed loop.
What are the different heat source options for radiant floor heating?
Depending on your specific requirements, you can choose from on-demand water heaters, tank-type water heaters, boilers, and electric units.
How do I determine the appropriate mixture and concentration of antifreeze for my radiant floor heating system?
Manufacturers provide guidelines for the appropriate mixture, and it is recommended to premix the antifreeze before pumping it into the system.
Why is maintaining proper pressure in the system necessary for radiant floor heating?
Maintaining proper pressure prevents air from entering the system, which can cause issues and should be purged during start-up.
When should I use a mixing valve in my radiant floor heating system?
A mixing valve is essential when the heat source supplies water at a higher temperature than the radiant floor requires. This ensures the water is tempered to a suitable temperature before entering the radiant system.
Should I install a whole house filter for my radiant floor heating system?
Installing a whole-house filter can protect components and plumbing fixtures in open systems from damage caused by the mineral content and additives in the water, such as chlorine.
What are some considerations for specific plumbing configurations in radiant floor heating systems?
High-volume systems and outdoor wood boilers require specific plumbing configurations, and following the recommended guidelines for these setups is essential.
How can efficient circulator pumps enhance the performance of my radiant floor heating system?
Efficient circulator pumps can significantly reduce energy costs and improve system performance.
What are the benefits of radiant floor heating?
Radiant floor heating systems offer energy efficiency, improved comfort, and design flexibility advantages.
How much does radiant floor heating cost?
The cost of installing and operating a radiant floor heating system depends on factors such as the size of the space, type of system, and chosen heat source. It is best to consult a professional to get an accurate cost estimate.
What maintenance practices are essential for a radiant floor heating system?
Regular maintenance, such as checking for proper pressure, purging air, and ensuring the system is debris-free, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Why is a radiant floor heating diagram helpful?
A radiant floor heating diagram can help you understand how the system works and the different components involved, allowing for better troubleshooting and maintenance.






